How to check MySQL Database Size
Updated on Jul 9, 2018
Relation between Database Size and Hardware Resources
As we explained in the Introductory section, in order for a typical MySQL database to exist, it should be stored on the file system of the Web Hosting Server. This means that a portion of the allocated space for each Web Hosting Package will be used by the MySQL databases maintained by the Shared Web Hosting users.
Furthermore, whenever a database gets queried by a web application, it uses a different amount of hardware resources like CPU, RAM, and I/O operations. These are required so the MySQL database management service can execute the query against the database and provide the result to the web application that sends it.
If the query targets large collection of rows (for example it selects all the rows in a table), then the MySQL service will require more resources to find and prepare the rows for the web application.
Therefore, we can surely say that the bigger a database is, the more resources the queries sent to it will need.
How to check your database size?
To check the sizes of your databases, you will need to access the cPanel service for the Web Hosting package you have purchased with us. You can find more details on how to do that in the Welcome email, or you can directly access it via the Dashboard of your Client Area using the cP labeled button next to the web hosting package you would like to maintain.
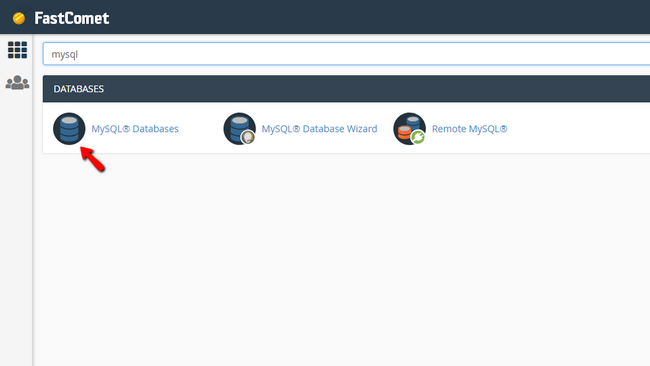
The cPanel service offers a vast amount of features, and you will need to locate the MySQL databases feature specifically. This can be done pretty easily by typing MySQL in the search bar of cPanel.
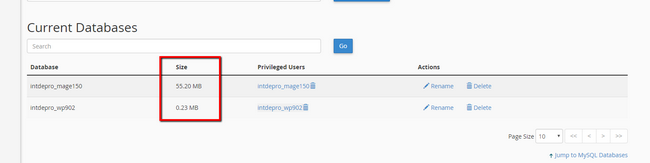
The MySQL Databases feature will offer few options separated in different sections. The section you are looking for here is called Current Databases where you will find a table populated with all the databases you currently have and more importantly their sizes.
Unfortunately, cPanel does not offer the option to order the databases by their actual size so please bear in mind that the databases in the table are by default sorted by name and not by size. Ideally you would want to show all the databases on a single page considering the pagination at the bottom of the Current Databases section.
Once you identify the big databases, you can go ahead and optimize their size which we will review in other tutorials of these Series.
Observer Reports
As we have mentioned there are certain limitations in regards to the database sizes for our Shared Web Hosting users. Depending on the used Web Hosting package the limitations are growing exponentially, but most importantly our customers will always be notified when reaching or being close to reaching a certain limit.
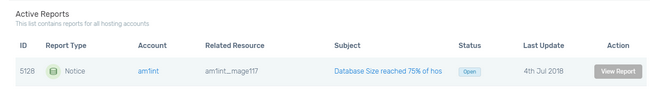
The system that takes care of reporting and resolving Web Hosting Limits related issues is called Observer and you might have already seen it in the Client Area section of our website.
Lifecycle of Observer Reports for Database size
To better understand how the Observer Reporting service works we will explain all the reports you will receive in regards to the size of your databases.
- Firstly, if any database on your web hosting account reaches 75% of the allowed size per database of the used Web Hosting Package, the Observer service will open a Notice type of Report providing detailed information for the Database Size limit.
- Secondly, if 90% or more of the allowed size per database is being reached the Observer service will open an Alert type of Report reminding the customer of the ongoing issue and the potential risk. If already reported as Notice database reaches 90% of the allowed size per database the Notice report will be updated and changed to Alert.
- Finally, if 100% of the allowed size per database is being reached the Observer service will open an Incident type of Report informing the customer that the web hosting package has reached it's potential. 72 hours after that report has been filed and if the customer does not take action, the system will update it with information that the Web Hosting Account has been temporarily put on hold due to its complete incapability of handling visitors' requests due to high resource usage caused by the big database it has.
Of course, the customer is provided with the option of temporarily re-activate his/her web hosting account. The temporary re-activation will provide the customer with access to the web hosting account for a limited amount of time so the database size issue can be addressed.

Optimized SSD Web Hosting
- Free Domain Transfer
- 24/7 Technical Support
- Fast SSD Storage
- Hack-free Protection
- Free Script Installation
- Free Website Transfer
- Free Cloudflare CDN
- Immediate Activation
