What is a MAC Address?
Updated on Dec 9, 2024
We all know of IP addresses—they identify network devices and ensure traffic goes the correct route! However, did you know there is another address that does something similar at a local level but is just as important? It is the Media Access Control (MAC) address.
A MAC address is still used for network communications and plays a vital role in data transfer. However, its purpose is solely related to local area networks. So, with that in mind, read on as we discuss in more detail what a MAC address is, its purpose, and how it differs from an IP address.
In This Post:
What is a MAC Address?
As we mentioned above, the Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier. However, in this case, it is assigned to a specific piece of hardware: a network interface controller (NIC). Before we go any further, let us elaborate on what an NIC is.
Every device that can connect to the Internet has an interface controller: computers, mobile devices, routers, etc. If you have a device that can connect to the Internet, then it definitely has an NIC. It is a hardware component within your device that facilitates either wired or wireless network connection. On modern-day computers, for example, it is the card you plug your Ethernet cable into. Without the NIC, your computer could not connect to the Internet.
Now that we know about that component, it is easy to explain a MAC address. It is the unique identifier for the network interface controller. It is composed of twelve hexadecimal digits, formatted in six pairs. What is hexadecimal? It is a numeral system made up of the numbers from 0 to 9, and then the letters from A to F. Here is an example MAC address to make it clearer: 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E.
The existence of this address is crucial to local area networks because there would be chaos and anarchy without it. Imagine your wireless router and all the Ethernet ports it has. Wirelessly or otherwise, every device connected to it is part of that router's local area network. Since each device has its own NIC and its own MAC, the router knows what traffic to send to which device. Without those two things, the router would not know who opens which website. You can imagine the mess that would occur.
Fortunately, because MAC addresses exist, the router knows precisely which device needs what data. As for why your router itself has a MAC address – since all online communication, not local, is handled by IPs, it is so that the router itself can be identified as part of your ISP's network. That way, it can be assigned an IP; through it, all local devices can connect to the Internet.
Speaking of IPs, let's talk about how they differ from MAC addresses.
Difference between IP and MAC
You might have already guessed the difference between these two addresses, but we will sum it up in this section for your convenience.
The difference between them lies in their scope, role, and the levels at which they operate in the networking model. The easiest way to compare them is this: a MAC address is a local identifier, while an IP address is a global identifier. Here are a few other key differences to deepen the comparison.
- Purpose - A MAC address is used to locate a device on a local network and route traffic to it. On the other hand, an IP address is for identifying a device on a larger network (such as the Internet) and ensuring the correct traffic goes to it;
- Scope of Use - In the OSI networking model, a MAC address works exclusively on the Data Link layer, enabling direct communication between devices on the same local network. An IP address operates on the Network layer, facilitating communication between devices on different networks across the Internet;
- Permanence - A MAC address is typically hardcoded into the NIC during manufacturing and very rarely, if ever, changes. An IP address, however, is assigned by the network (your ISP, for example) and can change depending on the network configuration;
- Format - Both addresses differ significantly not only in how they look but in how they are formulated as well;
- MAC - A MAC address is comprised of twelve hexadecimal digits, written in six pairs separated by colons (00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E);
- IP - There are two main formats for IP addresses. The first one is IPv4 (192.168.1.1), and the second is IPv6 (2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
As you can see, these two addresses have some significant differences, but their purpose is similar: identifying devices. One does it locally, the other does it globally.
Why is MAC Important?
While a MAC address' primary purpose is to identify devices in a local area network and facilitate the communication between them, it has several other essential functions.
- IP Assignment - In order for a device to communicate over the Internet, it needs an IP address. A MAC address is essential for the assignment of an IP. Firstly, the issuer of the IP (usually an ISP) uses the MAC address to find the exact device that needs the IP. Secondly, the MAC address keeps track of which device has which IP. That is important because that way when a device reconnects to a network, it gets the same IP it had before;
- Network Security - MAC Filtering is a tool available to network administrators, allowing them to allow or deny access to a network only for specific MAC addresses. Additionally, since MAC addresses are unique, administrators can keep track of who connects to a network and identify unwanted devices;
- Network Troubleshooting and Management - A MAC address allows administrators to identify and isolate problematic devices without affecting the entire local network. Additionally, administrators can manage local network traffic, monitor device activity, and, therefore, optimize network performance where necessary.
In essence, MAC addresses are foundational for the efficient functioning, security, and management of local networks. Data reaches the correct destination through them, unwanted devices are kept out of the network, and administrators can monitor its performance and make changes when needed.
How to Find Your MAC Address?
Finally, we will show you how to locate the MAC address on your device. If you are looking for the MAC address for your router, you do not even need to have it connected to the Internet. Typically, there will be a sticker on the back of it with the MAC address (and sometimes your Wi-Fi name and password). As for other types of devices, here is how you can find the address there.
- Windows 10/11
- Open the Start menu and type in Settings;
- Go to Network & Internet;
- On Windows 10, click Hardware and Connection Properties. On Windows 11, you have to click Advanced Network Settings first;
- Look for the Physical Address (MAC) line;
- Alternatively, you can open the command prompt and type in ipconfig /all and look for the physical address there, too;

- Linux
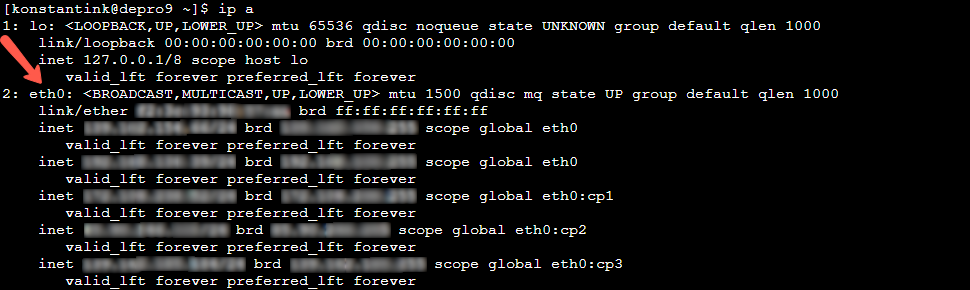
- Since there are many different Linux distributions, the easiest way to find your device's MAC is via the terminal. We are giving you a few commands you can run, in case one of them does not work. You are looking for the Ethernet line;
- ip a
- ipconfig
- ifconfig
- ip link
- Since there are many different Linux distributions, the easiest way to find your device's MAC is via the terminal. We are giving you a few commands you can run, in case one of them does not work. You are looking for the Ethernet line;
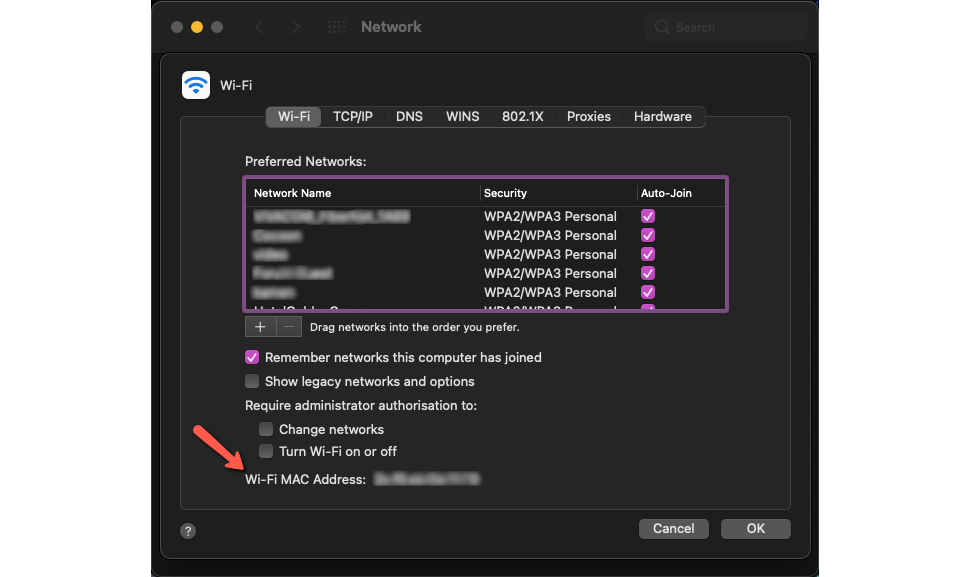
- MacOS
- Finding your MAC address on your MacOS device is very easy. Simply go to Settings>Network>Advanced, and you will find it there;
- iOS and Android
- When it comes to a smartphone, you can typically find your MAC address in the About section. Depending on your specific device and its OS version, the precise steps can vary;
- So, simply navigate to the About section of your phone (typically in the Settings application) and find the line that lists physical or MAC address.
It is not difficult to find your device's MAC address on any of them. That is because network administrators often work with those addresses, and looking for them through layers of menus would be a nightmare.
As you can see, the MAC address plays a vital role not only in identifying a device on a local network but also acts as an anchor for the IP address and serves a security and monitoring purpose. Without it, the network would be chaotic, and our devices would not be able to connect to the Internet efficiently.
We hope you find this article useful. Discover more about FastCloud - the top-rated Hosting Solutions for personal and small business websites in four consecutive years by the HostAdvice Community!

SSD Cloud Hosting
- Free Domain Transfer
- 24/7 Technical Support
- Fast SSD Storage
- Hack-free Protection
- Free Script Installation
- Free Website Transfer
- Free Cloudflare CDN
- Immediate Activation